PESTLE Analysis Explained with a Real Business Example
Written by Angela Iobst
A PESTLE analysis example helps organizations understand how external factors influence strategic decisions. Rather than focusing on internal operations, PESTLE analysis examines the broader environment a business operates within.
In this article, we explain the PESTLE framework and walk through a real business example to show how it works in practice.
What Is PESTLE Analysis?
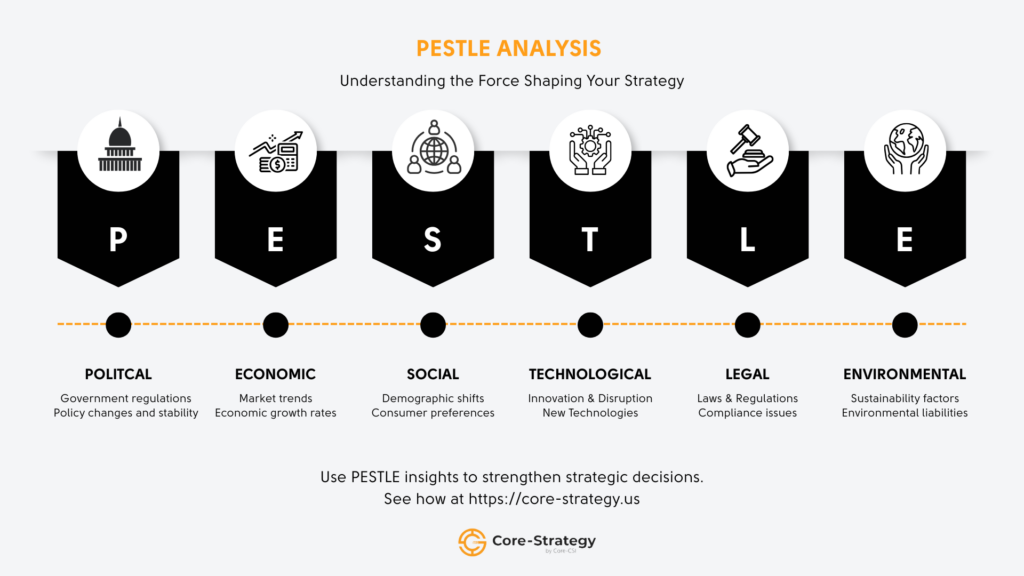
PESTLE analysis is a strategic framework used to analyze external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization.
The acronym stands for:
-
Political
-
Economic
-
Social
-
Technological
-
Legal
-
Environmental
Together, these factors help organizations identify risks, opportunities, and constraints beyond their direct control.
Why Companies Use PESTLE Analysis
Organizations use PESTLE analysis to:
-
Anticipate external risks
-
Identify emerging opportunities
-
Support long-term planning
-
Inform major strategic decisions
Unlike internal assessments, PESTLE analysis focuses on forces that shape the market environment as a whole.
PESTLE Analysis Example: Expanding into a New Market
To illustrate how the framework works, consider a mid-sized U.S. consumer goods company planning to expand into a new international market.
Leadership wants to understand whether external conditions support growth or introduce significant risk.
Political Factors
The company evaluates:
-
Government stability
-
Trade policies and tariffs
-
Regulatory oversight
-
Political relationships with the U.S.
Political uncertainty could affect supply chains or market access.
Economic Factors
Economic considerations include:
-
Inflation and interest rates
-
Currency stability
-
Consumer purchasing power
-
Overall economic growth
A volatile economy may reduce demand or increase operational costs.
Social Factors
Social analysis focuses on:
-
Consumer preferences
-
Cultural norms
-
Demographic trends
-
Lifestyle changes
Understanding local values helps the company adapt products and messaging effectively.
Technological Factors
The company reviews:
-
Digital infrastructure
-
Technology adoption rates
-
E-commerce maturity
-
Innovation trends
Strong technology infrastructure may support faster market entry and scalability.
Legal Factors
Legal considerations include:
-
Employment laws
-
Consumer protection regulations
-
Intellectual property rules
-
Compliance requirements
Failure to address legal risks can result in costly delays or penalties.
Environmental Factors
Environmental analysis examines:
-
Sustainability expectations
-
Environmental regulations
-
Climate-related risks
-
Resource availability
Increasing environmental standards may affect packaging, sourcing, or operations.
How the PESTLE Analysis Informs Strategy
After completing the PESTLE analysis, leadership uses the insights to:
-
Adjust market entry timing
-
Modify product offerings
-
Plan risk mitigation strategies
-
Align investment decisions with external realities
This structured approach helps leaders make informed choices rather than relying on assumptions.
PESTLE Analysis and Strategic Planning
PESTLE analysis is most effective when combined with broader strategic planning efforts. It often serves as a foundation for decisions related to growth, market entry, or transformation.
This type of external analysis is commonly used within strategy and management consulting to support evidence-based decision-making.
Final Thoughts
This PESTLE analysis example shows how organizations can systematically evaluate external forces that influence strategy.
By understanding political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors, leaders gain clarity, reduce risk, and make more confident strategic decisions.
Learn more at Core-Strategy.