Written by Angela Iobst
PESTLE Analysis: Understanding the Forces That Shape Strategy
PESTLE analysis is a strategic framework used in strategic planning to assess the external political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental forces shaping organizational decision-making.
In today’s volatile business environment, effective strategy starts with a clear understanding of these external influences. By systematically evaluating macro-environmental trends, leadership teams can anticipate risk, identify opportunity, and make better-informed strategic decisions.
Organizations such as the Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD) regularly analyze external political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental trends that align closely with PESTLE analysis.
This is where PESTLE analysis plays a critical role.
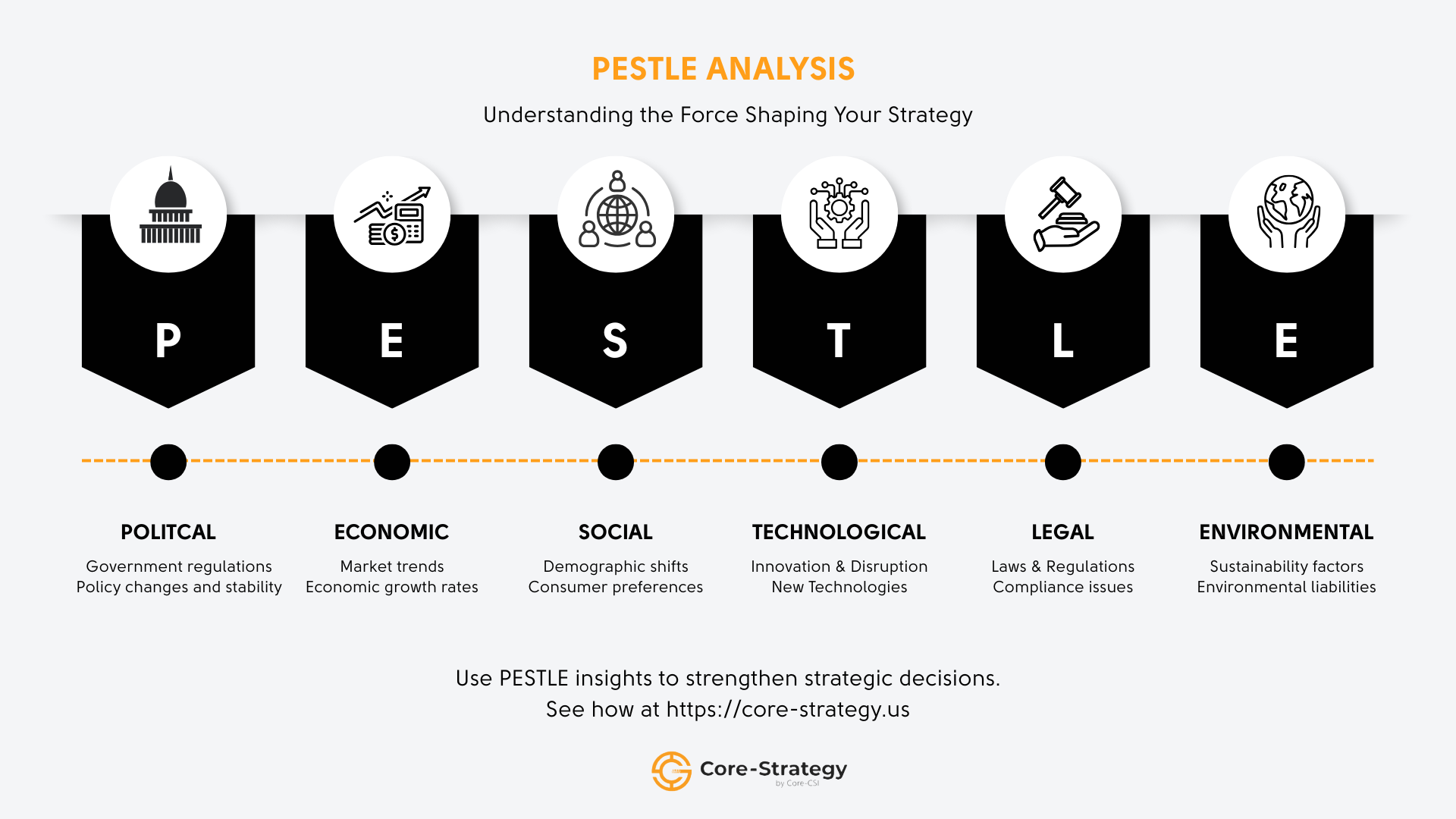
PESTLE analysis highlights the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental forces that shape strategic decisions.
What Is PESTLE Analysis?
PESTLE analysis is a macro-environmental assessment tool used during strategy formulation and strategic planning. Unlike internal analyses, PESTLE focuses on forces outside the organization’s control but critical to long-term success.
At Core-Strategy, we often use PESTLE analysis as a foundational input into:
-
Enterprise strategy formulation
-
Market entry and expansion decisions
-
Risk and regulatory assessments
-
Scenario planning and resilience strategies
When applied correctly, PESTLE analysis enables leadership teams to anticipate external risks and align strategy with a changing environment.
The Six Dimensions of PESTLE Analysis
1. Political Factors
Political forces shape the rules of the game in which organizations operate.
Key considerations include:
-
Government stability and policy direction
-
Taxation and trade policy
-
Public sector priorities and funding
-
Geopolitical risk
Political shifts can quickly alter market conditions, making proactive monitoring essential for leadership teams. Political and legal shifts introduce uncertainty that must be addressed through effective risk management and continuous environmental monitoring.
2. Economic Factors
Economic conditions influence demand, cost structures, and investment decisions.
Organizations should assess:
-
Economic growth trends
-
Inflation and interest rates
-
Labor market conditions
-
Access to capital
Understanding economic signals helps leaders align strategy with both short-term pressures and long-term cycles.
3. Social Factors
Social dynamics affect customers, employees, and broader stakeholder expectations.
Key social factors include:
-
Demographic shifts
-
Workforce expectations
-
Consumer behavior and preferences
-
Cultural and societal values
Ignoring social trends can lead to misaligned products, talent challenges, and reputational risk.
4. Technological Factors
Technology is one of the fastest-moving and most disruptive forces impacting strategy.
Areas to evaluate:
-
Emerging technologies and innovation cycles
-
Digital transformation trends
-
Automation and AI adoption
-
Cybersecurity risks
A strong PESTLE analysis ensures technology is treated as a strategic enabler — not just an operational issue.
5. Legal Factors
Legal and regulatory environments define compliance obligations and operational constraints.
Organizations must consider:
-
Industry-specific regulations
-
Employment and labor laws
-
Data protection and privacy requirements
-
Contractual and liability exposure
Early awareness of legal shifts allows organizations to reduce risk and avoid costly disruptions.
6. Environmental Factors
Environmental considerations are now central to strategy, not optional.
Key environmental factors include:
-
Environmental liabilities
-
Sustainability expectations
-
Resource constraints
Stakeholders increasingly expect organizations to address environmental risk and resilience as part of responsible leadership. This type of external environment analysis helps leaders anticipate long-term societal and environmental shifts.
How This Framework Strengthens Strategy Formulation
PESTLE analysis is most powerful when it informs strategic decision-making, not when external environment analysis exists as a standalone exercise.
At Core-Strategy, we integrate PESTLE insights into:
-
Strategy formulation and prioritization
-
Scenario planning and stress testing
-
Risk management frameworks
-
Executive decision support
By linking external analysis directly to strategic choices, organizations improve adaptability and long-term performance.
For a deeper exploration of strategic frameworks and executive decision tools, our collection of strategy and leadership eBooks provides additional perspective.
PESTLE Analysis vs. SWOT: What’s the Difference?
While often compared, PESTLE and SWOT serve different purposes.
-
PESTLE analysis focuses exclusively on external macro forces
-
SWOT analysis combines internal strengths and weaknesses with external opportunities and threats
Used together, they provide a comprehensive foundation for effective strategy formulation.
Applying PESTLE Analysis in Your Organization
To get value from PESTLE analysis:
-
Keep the analysis current — environments change quickly
-
Focus on strategic relevance, not exhaustive lists
-
Translate insights into clear strategic implications
-
Revisit assumptions regularly
Most importantly, ensure PESTLE analysis informs real decisions, not just documentation.
Strategic Insight Starts with External Awareness
This framework is a core input into effective strategy formulation for organizations navigating complex environments.
As a result, the PESTLE framework becomes a practical tool for strengthening long-term strategic decision-making.
This approach provides leaders with the structure needed to anticipate change and respond with confidence over the long term.
Additional perspectives on strategy, risk, and external change are regularly shared on our blog page.
To learn how Core-Strategy helps organizations apply proven frameworks like PESTLE analysis to real-world strategy challenges, visit core-strategy.us.
